NAFLD is the leading cause of chronic liver disease
NASH covers a wide spectrum of disease severity
RELATED NASH Definitions VIDEOS

NASH 2024: The New Nomenclature and Revised Definition
Dive into the transformative world of liver health with Prof. Vlad Ratziu’s enlightening insights on

Building a Better Future For Patients with NAFLD and NASH
On International NASH Day 2023, join Michael Betel of the Fatty Liver Alliance as he

Clinical Data Warehouse : definitions and use cases
Prof. Stéfan Darmoni, France, discusses the clinical data warehouses (CDW) where he explains its definitions

NAFLD: time to update the terminology? By Prof. S. Francque
2020 started with an important discussion about the terminology to be used regarding Non Alcoholic
RELATED NASH Definitions ARTICLES
Surveying Stigma: MAFLD’s Nomenclature from Patient and Provider Perspectives
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is estimated to affect 38% of adults worldwide, a statistic
Cardiovascular Disease in MASLD Patients: Mitigating Risks
The term metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) has recently been proposed as an alternative
Geographical burden of NAFLD: a review
Over the past few decades, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become a growing problem,
The new paradigm of cardiometabolic syndrome: a review
Cardiometabolic syndrome (CMS) involves a complex interplay of many issues, involving obesity, metabolic dysregulation, cardiovascular

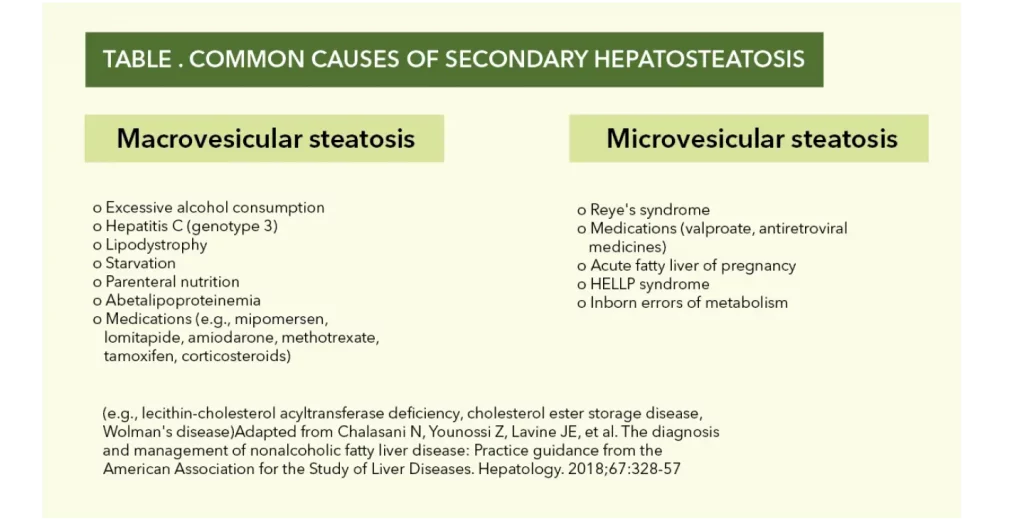
TABLE . COMMON CAUSES OF SECONDARY HEPATOSTEATOSIS
Macrovesicular Steatotis
- Excessive alcohol consumtion
- Hepatitis C (genotype 3)
- Lipodystrophy
- Starvation
- Parenteral nutrition
- Abetalipoproteinima
- Medications (e.g, mipomersen, lomitapide, amiodarene, methotrexate, tamoxifen, corticosteroids)
Macrovesicular Steatotis
- Reye's syndrome
- Medications ( valproate. antiretroviral, medicines)
- Acute fatty liver of preganacy
- HELLP Syndrome
- Inborn errors of metabolism
(e.g., lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferace deficiency, cholesterol ester storage disease, Wolman’s disease) Adapted from Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the study of Liver Disease. Hepatology. 2018;67:328-57
TABLE 1. Common Causes of Secondary Hepatosteatosis
• Macrovesicular steatosis
o Excessive alcohol consumption
o Hepatitis C (genotype 3)
o Lipodystrophy
o Starvation
o Parenteral nutrition
o Abetalipoproteinemia
o Medications (e.g., mipomersen, lomitapide, amiodarone, methotrexate, tamoxifen, corticosteroids)
• Microvesicular steatosis
o Reye’s syndrome
o Medications (valproate, antiretroviral medicines)
o Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
o HELLP syndrome
o Inborn errors of metabolism
(e.g., lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency, cholesterol ester storage disease, Wolman’s disease)
Adapted from Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67:328-57
References
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. 2018;67:328-57
- EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64:1388-402
- Stefan N, Häring HU, Cusi K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: causes, diagnosis, cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(4):313-324.
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease – Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73-84
- Younossi Z, Tacke F, Arrese M, et al. Global perspectives on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. 2019 Jun;69(6):2672-2682
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. 2018;67:328-57
- EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64:1388-402
- Stefan N, Häring HU, Cusi K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: causes, diagnosis, cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(4):313-324.
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease – Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73-84
- Younossi Z, Tacke F, Arrese M, et al. Global perspectives on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. 2019 Jun;69(6):2672-2682
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. 2018;67:328-57
- EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64:1388-402
- Stefan N, Häring HU, Cusi K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: causes, diagnosis, cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(4):313-324.
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease – Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73-84
- Younossi Z, Tacke F, Arrese M, et al. Global perspectives on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. 2019 Jun;69(6):2672-2682


