WHat is the NASH diagnosis criteria ?
For a positive diagnosis of NAFLD to be made, there should be
- Hepatic steatosis by imaging or histology
- No significant alcohol consumption
- No competing aetiologies for hepatic steatosis, such as hepatitis C, steatogenic drugs, parenteral nutrition, Wilson’s disease and severe malnutrition
- No coexisting causes of chronic liver disease, such as hemochromatosis, autoimmune liver disease, chronic viral hepatitis, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, Wilson’s disease and drug-induced liver injury
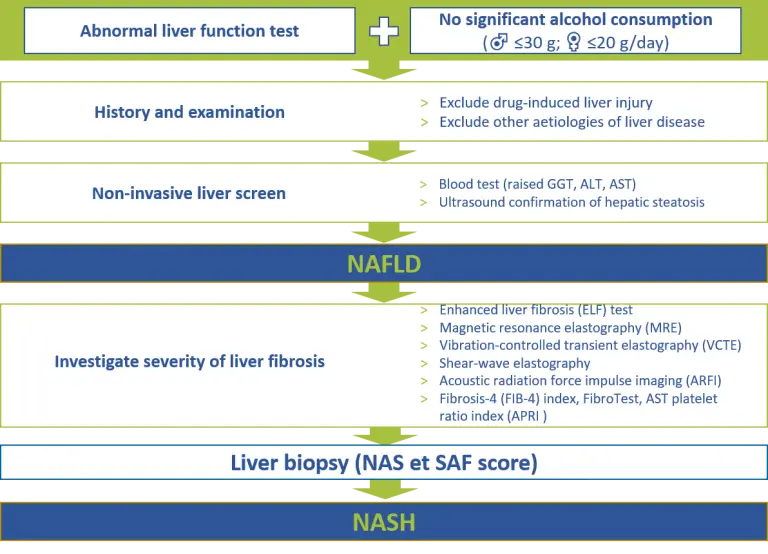
Once, a diagnosis of NAFLD has been established, patients should be assessed for NASH or fibrosis. While a liver biopsy remains the gold standard to differentiate NAFL from NASH and rule out other chronic liver diseases, elastography and scoring systems based on clinical features and routine biochemical testing can be used to assess fibrosis in patients with NAFLD and thus avoid invasive interventions that can be costly, risky, and potentially painful.
Current guidelines thus recommend that patients suspected of having NASH and/or steatohepatitis should undergo liver biopsy, as non-invasive techniques are expensive have not yet been validated. Biomarkers, fibrosis scores and electrography are recommended as acceptable non-invasive procedures for the identification of cases at low risk of advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis. New metabolomic biomarkers and genetic testing are currently under investigation.
RELATED NASH DIAGNOSIS VIDEOS

NASH 2024: The New Nomenclature and Revised Definition
Dive into the transformative world of liver health with Prof. Vlad Ratziu’s enlightening insights on

Clinical Chemistry In NAFLD Part 3 – Biomarkers and Hepatic Fibrosis
Discover the intricate dynamics of Clinical Chemistry in NAFLD with Dr. Guillaume Grzych, a leading

Clinical Chemistry in NAFLD Part 2 – Biomarkers, Hepatic Steatosis and NASH
Discover how key biomarkers like Fatty Liver Index and SteatoTest are transforming NAFLD diagnosis and

Clinical Chemistry in NAFLD Part 1 – Interest and Why?
Explore the complexities of NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease), now also known as MAFLD, and
RELATED NASH DIAGNOSIS ARTICLES
Screening, Diagnosis, and Staging of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Application of Society Guidelines to Clinical Practice
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), formerly known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has
Advancing Fibrosis Imaging: An Evaluation of Radiotracer Efficacy
Tissue fibrosis is induced by an excessive collagen deposition in organs suffering from inflammation and
Global research on fatty liver disease: a review
In this study, a large, global, multidisciplinary panel discussed priorities within the field of fatty
Discerning sex-related differences in NAFLD patients via metabolic profiling
Research into personalised medicine for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) underscores the importance of
Simplified algorithm for the diagnosis of NASH
- Bril F, Millan L, Kalavalapalli S, et al. Use of a metabolomic approach to non-invasively diagnose non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20:1702-09
- Byrne CD, Patel J, Scorletti E, Targher G. Tests for diagnosing and monitoring non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults. BMJ. 2018;362:k2734
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. 2018;67:328-57
- Gao F, Huang JF, Zheng KI, et al. Development and validation of a novel non-invasive test for diagnosing fibrotic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Oct;35(10):1804-1812.
- Imajo K, Kessoku T, Honda Y, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging more accurately classifies steatosis and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease than transient elastography. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:626-37 e7
- Toplak H, Stauber R, Sourij H. EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: guidelines, clinical reality and health economic aspects. Diabetologia. 2016;59:1148-9
- Younossi ZM, Noureddin M, Bernstein D, et al. Role of noninvasive tests in clinical gastroenterology practices to identify patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis at high risk of adverse outcomes: expert panel recommendations. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021 Feb 1;116(2):254-262.


